Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are a very common tumour in women. In the majority of cases they can grow to a large size without causing concern. Most women do not feel them and they go undetected.
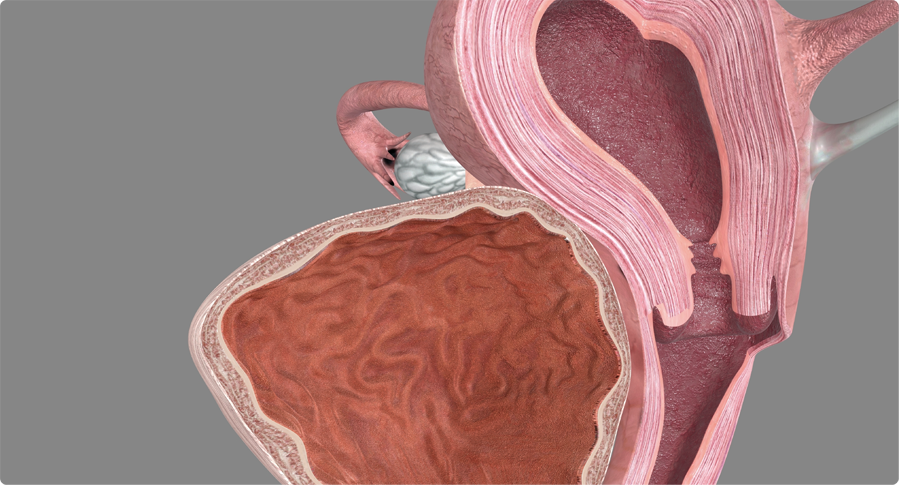
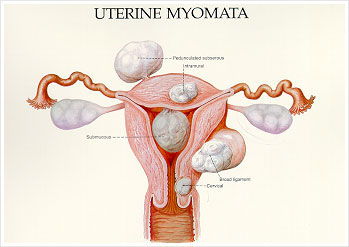
The location of the fibroid determines if they are felt or not.
| Subserous | - | arise from surface of uterus |
| Intramural | - | arises from the deeper muscle layer |
| Broad ligament | - | grows into side of uterus close to the major blood vessels of the uterus |
| Submucous | - | grows within the uterine cavity or close to the endometrium |
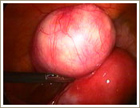
Subserous fibroids are those on the surface of the uterus and are the most common. These grow quite large without being felt. They are usually detected in the course of routine check ups.
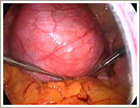
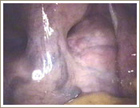
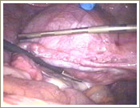

This group of fibroids tend to be the most often detected as they cause abnormal vaginal bleeding - periods can be prolonged, heavy or irregular in women with these fibroids. Fertility is another complaint. The presence of fibroids in the uterine cavity makes it difficult for the embryo to attach. This is described by a gynecologist (who happens to be a gardening enthusiast) as being similar to planting trees in a rock garden.
• Submucous Fibroids - Multiple• Submucous Fibroid - Single